java时间大小(java时间大小判断)
- 时间:
- 8422人关注
这是一篇关于java时间大小判断的编程热门专题内容,被971位程序员关注,内容涉及到java时间大小、java时间判断、java比较时间先后等,由郗笑寒编辑补充。
Java 日期与时间API相关用法总结
一、时间和日期
在系统开发中,日期与时间作为重要的业务因素,起到十分关键的作用,例如同一个时间节点下的数据生成,基于时间范围的各种数据统计和分析,集群节点统一时间避免超时等。
在时间和日期中有几个关键概念:
- 日期:通常年月日的组合表示当前日期。
- 时间:通常时分秒的组合表示当前时间。
- 时区:世界各国家与地区经度不同,划分24个标准时区,相邻时区的时间相差一个小时。
- 时间戳:从UTC时间的1970-1-1 00:00:00起到现在的总秒数。
日期和时间的用法在系统中通常是获取时间和一些常见的计算与格式转换处理,在一些垮时区的业务中就会变的复杂很多,例如在电商业务中的全球贸易或者海淘等。
二、JDK原生API
1、Date基础
基础用法
java.sql.Date继承java.util.Date,相关方法也大部分直接调用父类方法。
public class DateTime01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
java.util.Date data01 = new java.util.Date(nowTime);
java.sql.Date date02 = new java.sql.Date(nowTime);
System.out.println(data01);
System.out.println(date02.getTime());
}
}
打印:
Fri Jan 29 15:11:25 CST 2021
1611904285848
计算规则
public class DateTime02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date nowDate = new Date();
System.out.println("年:"+nowDate.getYear());
System.out.println("月:"+nowDate.getMonth());
System.out.println("日:"+nowDate.getDay());
}
}
年份:当前时间减去1900;
public int getYear() {
return normalize().getYear() - 1900;
}
月份:0-11表示1-12月份;
public int getMonth() {
return normalize().getMonth() - 1;
}
天份:正常表示;
public int getDay() {
return normalize().getDayOfWeek() - BaseCalendar.SUNDAY;
}
格式转换
非线程安全的日期转换API,该用法在规范的开发中是不允许使用的。
public class DateTime02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 默认转换
DateFormat dateFormat01 = new SimpleDateFormat() ;
String nowDate01 = dateFormat01.format(new Date()) ;
System.out.println("nowDate01="+nowDate01);
// 指定格式转换
String format = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat02 = new SimpleDateFormat(format);
String nowDate02 = dateFormat02.format(new Date()) ;
System.out.println("nowDate02="+nowDate02);
// 解析时间
String parse = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm";
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat03 = new SimpleDateFormat(parse);
Date parseDate = dateFormat03.parse("2021-01-18 16:59:59") ;
System.out.println("parseDate="+parseDate);
}
}
作为JDK初始版本就使用的日期和时间,Date类一直在项目中使用,但是相关API的方法都已经基本废弃,通常使用一些二次封装的时间组件。该API的设计堪称Java中的最烂。
2、Calendar升级
Calendar作为一个抽象类,定义日期时间相关转换与计算的方法,这个类目测
public class DateTime04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR,2021);
calendar.set(Calendar.MONTH,1);
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,12);
calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY,23);
calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE,59);
calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND,59);
calendar.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND,0);
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") ;
Date defDate = calendar.getTime();
System.out.println(defDate+"||"+dateFormat.format(defDate));
}
}
输出:Fri Feb 12 23:59:59 CST 2021||2021-02-12 23:59:59
直观感觉,Date中相关方法迁移Calendar实现,简化Date的功能侧重对日期与时间的实体封装,Calendar复杂相关计算策略,DateFormat依旧用来做格式处理。但是Calendar依旧很少被使用,上述基础API就已经是很好的说明了。
3、JDK1.8升级API
Java8之后的版本中,核心API类包括LocalDate-日期、LocalTime-时间、LocalDateTime-日期加时间。
- LocalDate:日期描述是final修饰的不可变类,默认格式yyyy-MM-dd。
- LocalTime:时间描述是final修饰的不可变类,默认格式hh:mm:ss.zzz。
- LocalDateTime:日期与时间描述final修饰的不可变类。
public class DateTime05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 日期:年-月-日
System.out.println(LocalDate.now());
// 时间:时-分-秒-毫秒
System.out.println(LocalTime.now());
// 日期时间:年-月-日 时-分-秒-毫秒
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now());
// 日期节点获取
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("[" + localDate.getYear() +
"年];[" + localDate.getMonthValue() +
"月];[" + localDate.getDayOfMonth()+"日]");
// 计算方法
System.out.println("1年后:" + localDate.plusYears(1));
System.out.println("2月前:" + localDate.minusMonths(2));
System.out.println("3周后:" + localDate.plusWeeks(3));
System.out.println("3天前:" + localDate.minusDays(3));
// 时间比较
LocalTime localTime1 = LocalTime.of(12, 45, 45); ;
LocalTime localTime2 = LocalTime.of(16, 30, 30); ;
System.out.println(localTime1.isAfter(localTime2));
System.out.println(localTime2.isAfter(localTime1));
System.out.println(localTime2.equals(localTime1));
// 日期和时间格式
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now() ;
LocalDate myLocalDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate();
LocalTime myLocalTime = localDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println("日期:" + myLocalDate);
System.out.println("时间:" + myLocalTime);
}
}
如果作为JodaTime组件的深度用户,对这个几个API使用基本无压力。
4、时间戳
时间戳也是业务中常用的方式,基于Long类型表示时间,在很多时候远比常规日期与时间的格式更好用。
public class DateTime06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 精确到毫秒级别
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(new Date().getTime());
System.out.println(Calendar.getInstance().getTime().getTime());
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.now().toInstant(
ZoneOffset.of("+8")).toEpochMilli());
}
}
这里需要注意的是在实际业务中由于获取时间戳的方式是多样的,所以建议统一工具方法,和规定精确度,避免部分精确到秒部分精确到毫秒的问题,这样可以规避在使用时相互转换的情况。
三、JodaTime组件
在Java8之前JodaTime组件是大部分系统中的常见选择,有很多方便好用的日期与时间的处理方法封装。
基础依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>joda-time</groupId> <artifactId>joda-time</artifactId> </dependency>
在joda-time提供的组件之上做一个简单的工具类封装,保证业务处理风格统一。
public class JodaTimeUtil {
// 时间格式
public static final String DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
private JodaTimeUtil (){}
// 获取当前时间
public static DateTime getCurrentTime (){
return new DateTime() ;
}
// 获取指定时间
public static DateTime getDateTime (Object obj){
return new DateTime(obj) ;
}
// 把时间以指定格式转换为字符串
public static String getNowDate (Date date, String format){
return new DateTime(date).toString(format) ;
}
// 获取星期时间
public static String getWeek (Object date){
DateTime time = getDateTime (date) ;
String week = null ;
switch (time.getDayOfWeek()) {
case DateTimeConstants.SUNDAY:
week = "星期日";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.MONDAY:
week = "星期一";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.TUESDAY:
week = "星期二";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.WEDNESDAY:
week = "星期三";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.THURSDAY:
week = "星期四";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.FRIDAY:
week = "星期五";
break;
case DateTimeConstants.SATURDAY:
week = "星期六";
break;
default:
break;
}
return week ;
}
}
四、源代码地址
GitHub·地址
https://github.com/cicadasmile/java-base-parent
GitEE·地址
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/java-base-parent
以上就是Java 日期与时间API相关用法总结的详细内容,更多关于Java 日期与时间api的资料请关注码农之家其它相关文章!
Java后端Cookie实现(时间戳)代码实例
我们来简单实现一个cookie。
一、简单介绍
Cookie 是一些数据, 存储于你电脑上的文本文件中。
当 web 服务器向浏览器发送 web 页面时,在连接关闭后,服务端不会记录用户的信息。
Cookie 的作用就是用于解决 "如何记录客户端的用户信息":
- 当用户访问 web 页面时,他的名字可以记录在 cookie 中。
- 在用户下一次访问该页面时,可以在 cookie 中读取用户访问记录
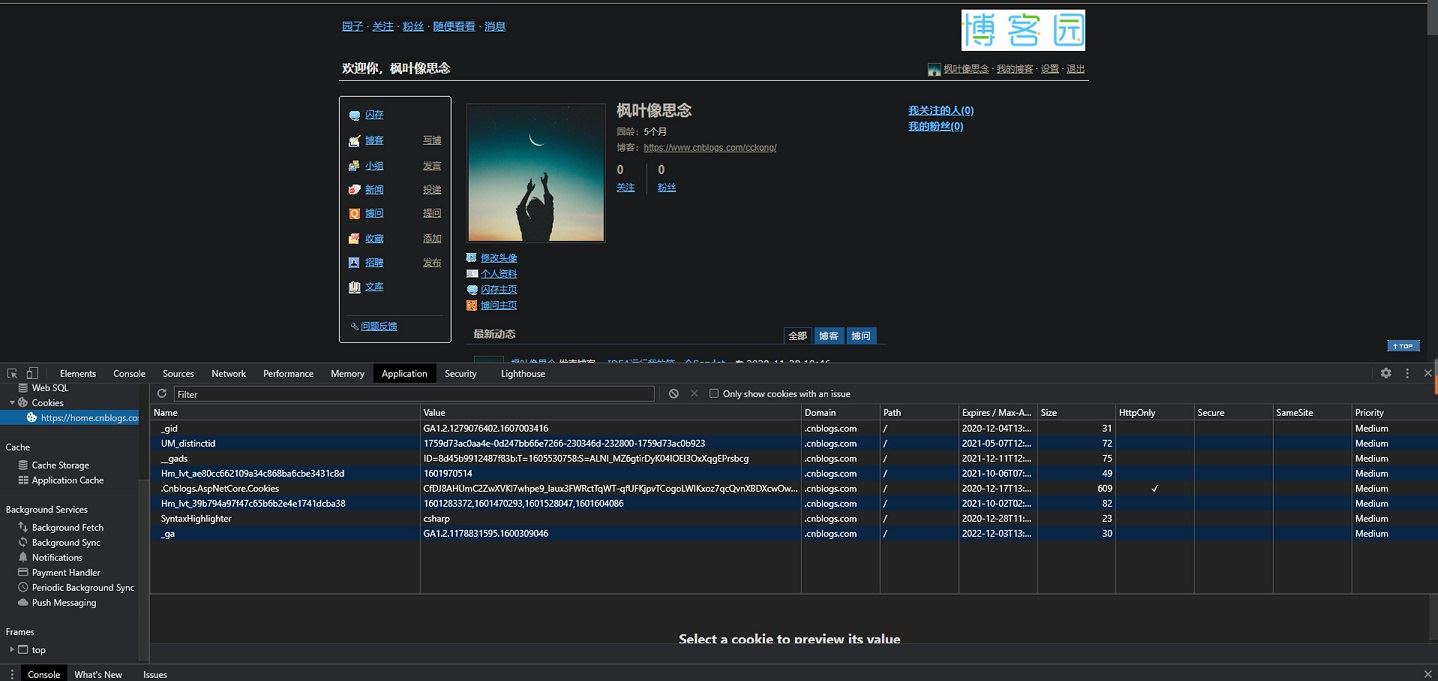
(博客园cookie界面)
二、简单实现
0.maven引入依赖
servlet和jsp的依赖
1.java代码编写
package com.lei;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Date;
public class CookieDemo01 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-16");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-16");
PrintWriter out =resp.getWriter();
Cookie[] cookies=req.getCookies();
if(cookies!=null)
{
out.write("您上一次访问时间为:");
for(int i=0;i< cookies.length;i++)
{
Cookie cookie=cookies[i];
if(cookie.getName().equals("lastLoginTime"))
{
long lastLoginTime=Long.parseLong(cookie.getValue());
Date date=new Date(lastLoginTime);
out.write(date.toString());
}
}
}
else{
out.write("first time come to this website!");
}
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("lastLoginTime",System.currentTimeMillis()+"");
resp.addCookie(cookie);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
2.设置web-xml里面加入 servlet注册和映射
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0"
metadata-complete="true">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>cookie</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.lei.CookieDemo01</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>cookie</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/cookie</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
三、运行效果
第一次cookie数组为空 不显示登陆时间
按理说应该会显示else里面的内容first time come to this website!
但是显示的是
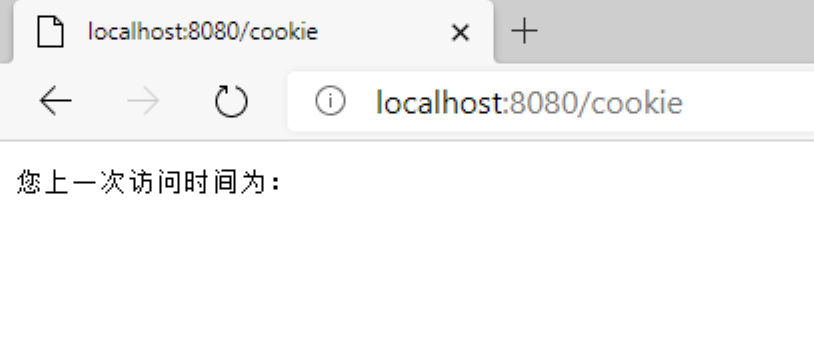
只是因为下面的第二张图 是因为浏览器(我的是edge浏览器)默认还有一个cookie
也就是说我们第一次在执行页面(如果是从8080页面输入url跳转的)时 有别的cookie存在
第二次才会显示
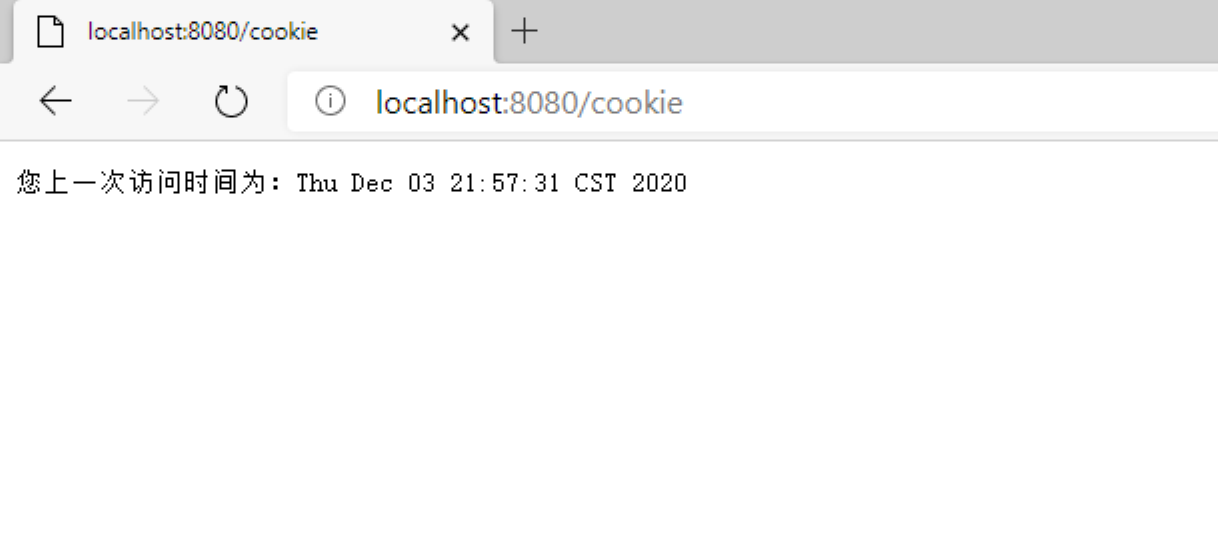
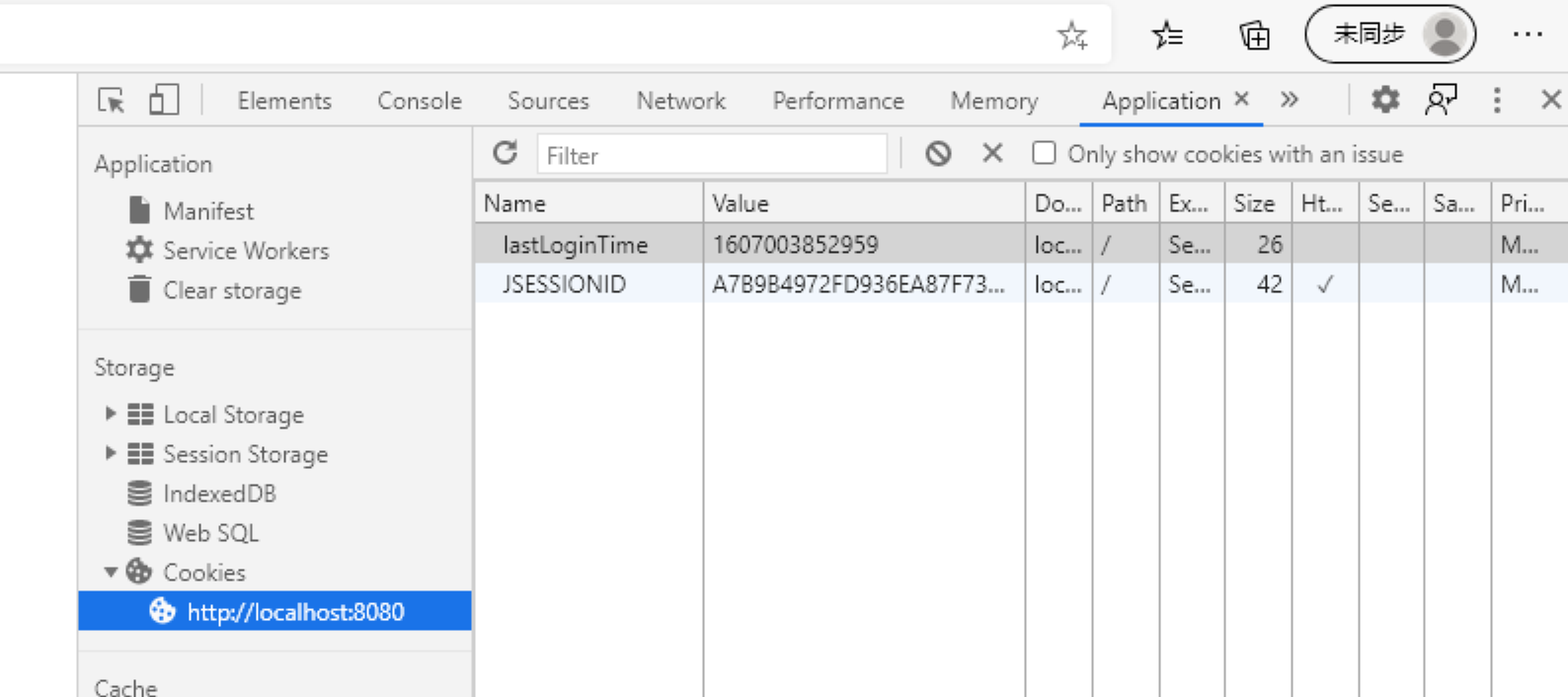
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持码农之家。
Java核心教程之常见时间日期的处理方法
Java日期处理类Date详解
时间的基础知识
- 时区:整个地球分为二十四时区,每个时区都有自己的本地时间。
- 为了统一起见,使用一个统一的时间,称为全球标准时间(UTC,Universal Time Coordinated)。
- TC与格林尼治平均时(GMT,Greenwich Mean Time,也翻译成:格林威治标准时间)差不多一样
- CST(北京时间),北京时间,China standard Time,中国标准时间。在时区划分上,属东八区,比协调世界时早8小时,记为UTC+8。
- 时间戳:自1970年1月1日(08:00:00GMT)至当前时间的总秒数,它也被称为Unix时间戳(unix Timestamp),广泛的运用在知识产权保护、合同签字、金融帐务、电子报价投标、股票交易等方面
- 格式多种:2050-10-3110:11:11、2050/10/3110/10:10年、月、日、周几等
背景:程序代码中怎么表示时间呢?我需要获取当前时间怎么办
ava.util包提供了Date类来封装当前的日期和时间
构造函数
//当前时间 Date() //从1970年1月1日起的毫秒数作为参数 Date(long millisec)
常见方法
//返回自1970年1月1日00:00:00GMT以来此Date对象表示的毫秒数。 long getTime() //调用此方法的Date对象在指定日期之后返回true,否则返回false。 boolean after(Date date) //调用此方法的Date对象在指定日期之前返回true,否则返回false。 boolean before(Date date)
新版JDK8之时间日期处理类
Java8通过发布新的Date-Time API(JSR310)来进一步加强对日期与时间的处理
新增了很多常见的api,如日期/时间的比较,加减,格式化等
包所在位置 java.time
核心类
LocalDate:不包含具体时间的日期。
LocalTime:不含日期的时间。
LocalDateTime:包含了日期及时间。
LocalDate常用API
LocalDate today=LocalDate.now(); system.out.print1n("今天日期:"+today); //获取年,月,日,周几 system.out.print1n("现在是哪年:"+today.getYear()); system.out.print1n("现在是哪月:"+today.getMonth()); System.out.print1n("现在是哪月(数字):"+today.getMonthValue()); System.out.print1n("现在是几号:"+today.getDayofMonth()); system.out.print1n("现在是周几:"+today.getDayofweek()); //加减年份,加后返回的对象才是修改后的,旧的依旧是旧的LocalDate changeDate=today.plusYears(1); system.out.print1n("加后是哪年:"+changeDate.getYear()); System.out.print1n("旧的是哪年:"+today.getYear()); //日期比较 system.out.print1n("isafter:"+changeDate.isAfter(today)); //getYear()int 获取当前日期的年份 //getMonth()Month获取当前日期的月份对象 //getMonthValue()int 获取当前日期是第几月 //getDayofweek()Dayofweek 表示该对象表示的日期是星期几 //getDayofMonth()int 表示该对象表示的日期是这个月第几天 //getDayofyear()int 表示该对象表示的日期是今年第几天 //withyear(int year)LocalDate 修改当前对象的年份 //withMonth(int month)LocalDate修改当前对象的月份 //withpayofMonth(int dayofMonth)LocalDate 修改当前对象在当月的日期 //plusYears(long yearsToAdd)Localpate 当前对象增加指定的年份数 //plusMonths(1ong monthsToAdd)LocalDate 当前对象增加指定的月份数 //plusweeks(1ong weeksToAdd)LocalDate 当前对象增加指定的周数 //plusDays(1ong daysToAdd)LocalDate 当前对象增加指定的天数 //minusYears(long yearsTosubtract)LocalDate 当前对象减去指定的年数 //minusMonths(1ong months ToSubtract)LocalDate当前对象减去注定的月数 //minusWeeks(long weeksTosubtract)LocalDate 当前对象减去指定的周数 //minusDays(1ong daysTosubtract)LocalDate当前对象减去指定的天数 //compareTo(ChronoLocalDate other)int 比较当前对象和other对象在时间上的大小,返回值如果为正,则当前对象时间较晚 //isBefore(ChronoLocalDate other)boolean比较当前对象日期是否在other对象日期之前 //isAfter(ChronoLocalDate other)boolean 比较当前对象日期是否在other对象日期之后 //isEqual(ChronoLocalDate other)boolean 比较两个日期对象是否相等
新版JDK8之时间日期格式化
为什么要时间日期做格式化
- 程序打印,或者网页显示时间日期格式,用户有不同的需求,则需要根据一定的规则进行格式化
常用的占位符
- y四位数年份
- M月d日
- h时在
- m分
- S毫秒
JDK8之后:引入线程安全的日期与时
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(ldt);
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd
HH:mm:ss");
String ldtStr = dtf.format(ldt);
System.out.println(ldtStr);
获取指定的日期时间对象LocalDate Time ldt=LocalDate Time.of(2020,11,11,8,20,30);System.out.println(ldt);
计算日期时间差 java.time.Duration
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(today); LocalDateTime changeDate = LocalDateTime.of(2020,10,1,10,40,30); System.out.println(changeDate); Duration duration = Duration.between( today,changeDate);//第⼆二个参数减第⼀一 个参数 System.out.println(duration.toDays());//两个时间差的天数 System.out.println(duration.toHours());//两个时间差的小时数 System.out.println(duration.toMinutes());//两个时间差的分钟数 System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//两个时间差的毫秒数 System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//两个时间差的纳秒数
总结
到此这篇关于Java核心教程之常见时间日期的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java常见时间日期内容请搜索码农之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持码农之家!
Java8新特性之新日期时间库的使用教程
一、为什么引入新的日期时间库
Java对日期,日历及时间的处理一直以来都饱受诟病,尤其是它决定将java.util.Date定义为可修改的以及将SimpleDateFormat实现成非线程安全的。
关于这个新的时间日期库的最大的优点就在于它定义清楚了时间日期相关的一些概念,比方说,瞬时时间(Instant),持续时间(duration),日期(date),时间(time),时区(time-zone)以及时间段(Period)。同时它也借鉴了Joda库的一些优点,比如将人和机器对时间日期的理解区分开的。Java 8仍然延用了ISO的日历体系,并且与它的前辈们不同,java.time包中的类是不可变且线程安全的。
二、如何使用Java8的新日期和时间
首先认识下Java8新日期和时间的一些关键类:
| 类名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Instant | 代表时间戳 |
| LocalDate | 不包含具体时间的日期 |
| LocalTime | 不包含日期的时间 |
| LocalDateTime | 包含了日期及时间,没有时区信息 |
| ZonedDateTime | 包含时区的完整的日期时间,偏移量是以UTC/格林威治时间为基准的 |
| DateTimeFormatter | 日期解析和格式化工具类 |
接下来从几个示例中认识Java8新日期和时间的特别之处,很强大
在Java8中获取当前日期
Java 8中有一个叫LocalDate的类,它能用来表示今天的日期。这个类与java.util.Date略有不同,因为它只包含日期,没有时间。因此,如果你只需要表示日期而不包含时间,就可以使用它。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("Today is : " + today);
输出结果:
Today is : 2020-12-13
从输出结果中可以看到,日期是格式化完了后再输出来的,不像之前的Date类那样,打印出来的数据都是未经格式化的,不便于阅读。
在Java8中获取当前的年月日
LocalDate类中提供了一些很方便的方法可以用于提取出年月日以及其它的日期属性。使用这些方法,你可以获取到任何你所需要的日期属性,而不再需要使用java.util.Calendar这样的类
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
int year = today.getYear();
int month = today.getMonthValue();
int day = today.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.printf("Year : %d , Month : %d , day : %d \t %n", year, month, day);
输出结果:
Year : 2020 , Month : 12 , day : 13
在Java8中获取某个特定的日期
使用工厂方法LocalDate.of(),则可以创建出任意一个日期,它接受年月日的参数,然后返回一个等价的LocalDate实例。关于这个方法还有一个好消息就是它没有再犯之前API中的错,比方说,年只能从1900年开始,月必须从0开始,等等。这里的日期你写什么就是什么,比如说,下面这个例子中它代表的就是1月14日,没有什么隐藏逻辑
LocalDate today = LocalDate.of(2020, 12, 13);
System.out.println("Today is : " + today);
输出结果:
Today is : 2020-12-13
在Java8中检查两个日期是否相等
LocalDate重写了equals方法来进行日期的比较
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2014, 01, 14);
if(date.equals(today)){
System.out.printf("Today %s and date %s are same date %n", today, date);
}
输出结果:
Today 2020-12-13 and date 2020-12-13 are same date
在Java8中检查重复事件
使用MonthDay类。这个类由月日组合,不包含年信息,也就是说你可以用它来代表每年重复出现的一些日子。当然也有一些别的组合,比如说YearMonth类。它和新的时间日期库中的其它类一样也都是不可变且线程安全的,并且它还是一个值类(value class)
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate dateOfBirth = LocalDate.of(2020, 12, 13);
MonthDay birthday = MonthDay.of(dateOfBirth.getMonth(), dateOfBirth.getDayOfMonth());
MonthDay currentMonthDay = MonthDay.from(today);
if (currentMonthDay.equals(birthday)) {
System.out.println("Oh, today is your birthday");
} else {
System.out.println("Sorry, today is not your birthday");
}
输出结果:
Oh, today is your birthday
在Java8中获取当前时间
使用LocalTime的类,它是没有日期的时间,与LocalDate是近亲。这里你也可以用静态工厂方法now()来获取当前时间。默认的格式是hh:mm:ss:nnn,这里的nnn是纳秒
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("local time now : " + time);
输出结果:
local time now : 13:44:48.255
在Java8中增加小时数
Java 8不仅提供了不可变且线程安全的类,它还提供了一些更方便的方法譬如plusHours()来替换原来的add()方法。顺便说一下,这些方法返回的是一个新的LocalTime实例的引用,因为LocalTime是不可变的,可别忘了存储好这个新的引用。
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
LocalTime newTime = time.plusHours(2);
System.out.println("Time after 2 hours : " + newTime);
输出结果:
Time after 2 hours : 15:47:00.787
在Java8中获取1周后的日期
LocalDate是用来表示无时间的日期的,它有一个plus()方法可以用来增加日,星期,或者月,ChronoUnit则用来表示这个时间单位。由于LocalDate也是不可变的,因此任何修改操作都会返回一个新的实例,因此别忘了保存起来。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate nextWeek = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);
System.out.println("Today is : " + today);
System.out.println("Date after 1 week : " + nextWeek);
输出结果:
Today is : 2020-12-13
Date after 1 week : 2020-12-20
在Java8中获取一年前后的日期
使用LocalDate的plus()方法来给日期增加日,周或者月,现在我们来学习下如何用minus()方法来找出一年前的那天。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate previousYear = today.minus(1, ChronoUnit.YEARS);
System.out.println("Date before 1 year : " + previousYear);
LocalDate nextYear = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.YEARS);
System.out.println("Date after 1 year : " + nextYear);
输出结果:
Date before 1 year : 2019-12-13
Date after 1 year : 2021-12-13
在Java8中使用时钟
Java 8中自带了一个Clock类,你可以用它来获取某个时区下当前的瞬时时间,日期或者时间。可以用Clock来替代System.currentTimeInMillis()与 TimeZone.getDefault()方法,如果你需要对不同时区的日期进行处理的话这是相当方便的。
// Returns the current time based on your system clock and set to UTC.
Clock clock1 = Clock.systemUTC();
System.out.println("Clock : " + LocalDate.now(clock1));
// Returns time based on system clock zone Clock defaultClock =
Clock clock2 = Clock.systemDefaultZone();
System.out.println("Clock : " + LocalDate.now(clock2));
输出结果:
Clock : 2020-12-13
Clock : 2020-12-13
在Java8中判断一个日期在某个日期的前后
在Java 8中,LocalDate类有一个isBefore()和isAfter()方法可以用来比较两个日期。如果调用方法的那个日期比给定的日期要早的话,isBefore()方法会返回true。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate tomorrow = LocalDate.of(2020, 12, 14);
if (tomorrow.isAfter(today)) {
System.out.println("Tomorrow comes after today");
}
LocalDate yesterday = today.minus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
if (yesterday.isBefore(today)) {
System.out.println("Yesterday is day before today");
}
输出结果:
Tomorrow comes after today
Yesterday is day before today
在Java8中处理不同的时区
Java 8不仅将日期和时间进行了分离,同时还有时区。现在已经有好几组与时区相关的类了,比如ZonId代表的是某个特定的时区,而ZonedDateTime代表的是带时区的时间。
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime dateAndTimeInNewYork = ZonedDateTime.of(localDateTime, ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
System.out.println("Current date and time in a particular timezone : " + dateAndTimeInNewYork);
输出结果:
Current date and time in a particular timezone : 2020-12-13T14:40:44.664-05:00[America/New_York]
在Java8中表示固定的日期
YearMonth又是另一个组合,它代表的是像信用卡还款日,定期存款到期日,options到期日这类的日期。你可以用这个类来找出那个月有多少天,lengthOfMonth()这个方法返回的是这个YearMonth实例有多少天,这对于检查2月到底是28天还是29天可是非常有用的。
YearMonth currentYearMonth = YearMonth.now();
System.out.printf("Days in month year %s: %d%n", currentYearMonth, currentYearMonth.lengthOfMonth());
YearMonth creditCardExpiry = YearMonth.of(2020, Month.FEBRUARY);
System.out.printf("Your credit card expires on %s %n", creditCardExpiry);
输出结果:
Days in month year 2020-12: 31
Your credit card expires on 2020-02
在Java8中检查闰年
LocalDate类有一个isLeapYear()的方法能够返回当前LocalDate对应的那年是否是闰年。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
if (today.isLeapYear()) {
System.out.println("This year is Leap year");
} else {
System.out.println("2020 is not a Leap year");
}
输出结果:
This year is Leap year
在Java8中判断两个日期之间包含多少天/月
一个常见的任务就是计算两个给定的日期之间包含多少天,多少周或者多少年。你可以用java.time.Period类来完成这个功能。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate java8Release = LocalDate.of(2021, Month.JANUARY, 13);
Period periodToNextJavaRelease = Period.between(today, java8Release);
System.out.println("Months left between today and Java 8 release : " + periodToNextJavaRelease.getMonths());
输出结果:
Months left between today and Java 8 release : 1
在Java8中获取当前时间戳
Instant类有一个静态的工厂方法now()可以返回当前时间戳
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
System.out.println("instant : " + timestamp);
输出结果:
instant : 2020-12-13T07:30:55.877Z
在Java8中使用预定义的格式器来对日期进行解析/格式化
在Java 8之前,时间日期的格式化可是个技术活,我们的好伙伴SimpleDateFormat并不是线程安全的,而如果用作本地变量来格式化的话又显得有些笨重。多亏了线程本地变量,这使得它在多线程环境下也算有了用武之地。这次它引入了一个全新的线程安全的日期与时间格式器。它还自带了一些预定义好的格式器,包含了常用的日期格式。
String date = "20201213";
LocalDate formatted = LocalDate.parse(date, DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE);
System.out.printf("Date generated from String %s is %s %n", date, formatted);
输出结果:
Date generated from String 20201213 is 2020-12-13
在Java8中使用自定义的格式器来解析日期
在DateTimeFormatter的ofPattern静态方法()传入任何的模式,它会返回一个实例,这个模式的字面量与前例中是相同的。比如说M还是代表月,而m仍是分。无效的模式会抛出DateTimeParseException异常
String goodFriday = "12 13 2020";
try {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("MM dd yyyy");
LocalDate holiday = LocalDate.parse(goodFriday, formatter);
System.out.printf("Successfully parsed String %s, date is %s%n", goodFriday, holiday);
} catch (DateTimeParseException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
输出结果:
Successfully parsed String 12 13 2020, date is 2020-12-13
在Java8中对日期进行格式化,转换成字符串
使用DateTimeFormatter类的实例,调用它的format()方法。这个方法会返回一个代表当前日期的字符串,对应的模式就是传入的DateTimeFormatter实例中所定义好的。
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("MMM dd yyyy hh:mm a");
String landing = localDateTime.format(format);
System.out.printf("Arriving at : %s %n", landing);
输出结果:
Arriving at : 十二月 13 2020 04:13 下午
三、总结
- Java 8中新的时间与日期API中的所有类都是不可变且线程安全的,这与之前的Date与Calendar API中的恰好相反,那里面像java.util.Date以及SimpleDateFormat这些关键的类都不是线程安全的。
- 新的时间与日期API中很重要的一点是它定义清楚了基本的时间与日期的概念,比方说,瞬时时间,持续时间,日期,时间,时区以及时间段。它们都是基于ISO日历体系的。
- Java8新的API能胜任任何与时间日期相关的任务。
到此这篇关于Java8新特性之新日期时间库使用的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java8新日期时间库内容请搜索码农之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持码农之家!
java 获取当前时间的三种方法
总结java里面关于获取当前时间的一些方法
System.currentTimeMillis()
获取标准时间可以通过System.currentTimeMillis()方法获取,此方法不受时区影响,得到的结果是时间戳格式的。例如:
1543105352845
我们可以将时间戳转化成我们易于理解的格式
SimpleDateFormat formatter= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(formatter.format(date));
则该时间戳对应的时间为:
2018-11-25 at 01:22:12 CET
值得注意的是,此方法会根据我们的系统时间返回当前值,因为世界各地的时区是不一样的。
java.util.Date
在Java中,获取当前日期最简单的方法之一就是直接实例化位于Java包java.util的Date类。
Date date = new Date(); // this object contains the current date value
上面获取到的日期也可以被format成我们需要的格式,例如:
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(formatter.format(date));
Calendar API
Calendar类,专门用于转换特定时刻和日历字段之间的日期和时间。
使用Calendar 获取当前日期和时间非常简单:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); // gets current instance of the calendar
与date一样,我们也可以非常轻松地format这个日期成我们需要的格式
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(formatter.format(calendar.getTime()));
上面代码打印的结果如下:
25-11-2018 00:43:39
Date/Time API
Java 8提供了一个全新的API,用以替换java.util.Date和java.util.Calendar。Date / Time API提供了多个类,帮助我们来完成工作,包括:
- LocalDate
- LocalTime
- LocalDateTime
- ZonedDateTime
- LocalDate
LocalDate只是一个日期,没有时间。 这意味着我们只能获得当前日期,但没有一天的具体时间。
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now(); // gets the current date
我们可以format它
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy");
System.out.println(date.format(formatter));
得到的结果只有年月日,例如:
25-11-2018
LocalTime
LocalTime与LocalDate相反,它只代表一个时间,没有日期。 这意味着我们只能获得当天的当前时间,而不是实际日期:
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now(); // gets the current time
可以按如下方式format
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(time.format(formatter));
得到的结果类似如下:
00:55:58
LocalDateTime
最后一个是LocalDateTime,也是Java中最常用的Date / Time类,代表前两个累的组合 - 即日期和时间的值:
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); // gets the current date and time
format的方式也一样
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(dateTime.format(formatter));
得到的日期结果类似于:
25-11-2018 00:57:20
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的java 获取当前时间的三种方法,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对码农之家网站的支持!
如果你觉得本文对你有帮助,欢迎转载,烦请注明出处,谢谢!
Javascript实现时间倒计时效果
本文实例为大家分享了js实现时间倒计时展示的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
这里使用的是Date日期类
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>日期类倒计时</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload=function(){
var odiv=document.getElementById("time");
var obtn=document.getElementById("btn");
var omusic=document.getElementById("music");
obtn.onclick=function(){//按钮点击 音乐停止播放
omusic.pause();
}
function totwo(e){
return e<10?"0"+e:""+e;//如果取得的数字为个数则在其前面增添一个0
}
function go(){//把获取时间的功能封装到函数内 注意 时间要向下取整避免小数
var time1=new Date();//获取当前时间 获取的市1970年1年1月日到现在的毫秒数(必须写在函数或者定时器内 每一次变化都要重新获取当前时间)
var time2=new Date(2017,9,27,17,20,10);//设置需要到达的时间 也是获取的毫秒数
var conS=Math.floor((time2.getTime()-time1.getTime())/1000);//获得差值除以1000转为秒
var day=totwo(Math.floor(conS/86400));// 差值/60/60/24获取天数
var hour=totwo(Math.floor(conS%86400/3600)); // 取余/60/60获取时(取余是获取conS对应位置的小数位)
var min=totwo(Math.floor(conS%86400%3600/60));// 取余/60获取分
var s=totwo(Math.floor(conS%60)); //取总秒数的余数
var html="倒计时"+day+"天"+hour+"时"+min+"分"+s+"秒";
odiv.innerHTML=html;//把字符串添加进div中
if(conS<0){//倒计时完成 执行功能,这里是播放MP3
clearInterval(time);//执行功能时要清除时间函数
omusic.play();
odiv.innerHTML="春节快乐!";
}
}
go();//调用函数
var time=setInterval(go,1000);//设置定时器 每一秒执行一次
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">停止</button>
<audio src="music.mp3" id="music"></audio>
<div id="time"></div>
</body>
</html>
效果图:
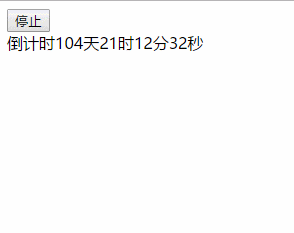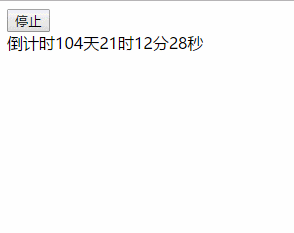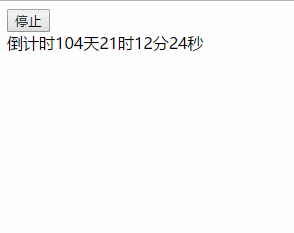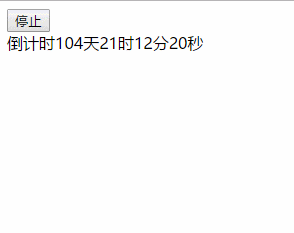
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持码农之家。
PHP与Java对比学习日期时间函数
废话少说先来看PHP中
date():格式化一个本地时间或者日期,当前时间 2016年5月13日 15:19:49
使用函数date(),输出当前是月份中的第几天,参数:String类型 d
例如:echo date("d"); 输出 13
使用函数date(),输出当前是星期中的第几天,参数:String类型 D或者 N
例如:
echo date("D"); 输出 Fri
echo date("N"); 输出 5
echo date("l"); 输出 Friday
使用函数date(),输出当前月份中的第几月,参数:String类型 n
echo date("n"); 输出 5
使用函数date(),判断当前年份是否是闰年,参数:String类型 L
echo date("L"); 输出 1
strtotime():把字符串类型日期格式转成时间戳
使用函数strtotime(),打印前一天日期,参数:String类型 “-1 day”
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("-1day"));输出 2016-05-12 15:27:33
使用函数strtotime(),打印明天日期,参数:String类型 “+1 day”
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("+1 day"));输出 2016-05-14 15:28:29
使用函数strtotime(),打印下周日期,参数:String类型 “+1 week”
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("+1 week"));;输出 2016-05-20 15:29:35
使用函数strtotime(),打印下一个月日期,参数:String类型 “+1 month”
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("+1 month")); 输出:2016-06-13 15:37:42
使用函数strtotime(),打印下周一日期,参数:String类型 “last Mondy”
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("next Monday")); 输出:2016-05-16 00:00:00
使用函数strtotime(),打印下周零两天两小时两秒后日期,参数:String类型组合一下
echo date("Y-m-d H:i:s",strtotime("+1 week 2 day 2 hour")); 输出 2016-05-22 17:34:34
==================================================================
java版:
java.util.Date类
获取Date对象,new出来
调用Date对象的getTime()方法,获取时间戳(毫秒值)
java.text.SimpleDateFormat类
获取SimpleDateFormat对象,new出来,构造参数:"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"
调用SimpleDateFormat对象的format()方法,获取String类型的日期,参数:Date对象
例如:
Date date=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
System.out.println(format.format(date));
java简单手写版本实现时间轮算法
时间轮
关于时间轮的介绍,网上有很多,这里就不重复了
核心思想
- 一个环形数组存储时间轮的所有槽(看你的手表),每个槽对应当前时间轮的最小精度
- 超过当前时间轮最大表示范围的会被丢到上层时间轮,上层时间轮的最小精度即为下层时间轮能表达的最大时间(时分秒概念)
- 每个槽对应一个环形链表存储该时间应该被执行的任务
- 需要一个线程去驱动指针运转,获取到期任务
以下给出java 简单手写版本实现
代码实现
时间轮主数据结构
/**
* @author apdoer
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/3/22 19:31
*/
@Slf4j
public class TimeWheel {
/**
* 一个槽的时间间隔(时间轮最小刻度)
*/
private long tickMs;
/**
* 时间轮大小(槽的个数)
*/
private int wheelSize;
/**
* 一轮的时间跨度
*/
private long interval;
private long currentTime;
/**
* 槽
*/
private TimerTaskList[] buckets;
/**
* 上层时间轮
*/
private volatile TimeWheel overflowWheel;
/**
* 一个timer只有一个delayqueue
*/
private DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> delayQueue;
public TimeWheel(long tickMs, int wheelSize, long currentTime, DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> delayQueue) {
this.currentTime = currentTime;
this.tickMs = tickMs;
this.wheelSize = wheelSize;
this.interval = tickMs * wheelSize;
this.buckets = new TimerTaskList[wheelSize];
this.currentTime = currentTime - (currentTime % tickMs);
this.delayQueue = delayQueue;
for (int i = 0; i < wheelSize; i++) {
buckets[i] = new TimerTaskList();
}
}
public boolean add(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
long expiration = entry.getExpireMs();
if (expiration < tickMs + currentTime) {
//到期了
return false;
} else if (expiration < currentTime + interval) {
//扔进当前时间轮的某个槽里,只有时间大于某个槽,才会放进去
long virtualId = (expiration / tickMs);
int index = (int) (virtualId % wheelSize);
TimerTaskList bucket = buckets[index];
bucket.addTask(entry);
//设置bucket 过期时间
if (bucket.setExpiration(virtualId * tickMs)) {
//设好过期时间的bucket需要入队
delayQueue.offer(bucket);
return true;
}
} else {
//当前轮不能满足,需要扔到上一轮
TimeWheel timeWheel = getOverflowWheel();
return timeWheel.add(entry);
}
return false;
}
private TimeWheel getOverflowWheel() {
if (overflowWheel == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (overflowWheel == null) {
overflowWheel = new TimeWheel(interval, wheelSize, currentTime, delayQueue);
}
}
}
return overflowWheel;
}
/**
* 推进指针
*
* @param timestamp
*/
public void advanceLock(long timestamp) {
if (timestamp > currentTime + tickMs) {
currentTime = timestamp - (timestamp % tickMs);
if (overflowWheel != null) {
this.getOverflowWheel().advanceLock(timestamp);
}
}
}
}
定时器接口
/**
* 定时器
* @author apdoer
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/3/22 20:30
*/
public interface Timer {
/**
* 添加一个新任务
*
* @param timerTask
*/
void add(TimerTask timerTask);
/**
* 推动指针
*
* @param timeout
*/
void advanceClock(long timeout);
/**
* 等待执行的任务
*
* @return
*/
int size();
/**
* 关闭服务,剩下的无法被执行
*/
void shutdown();
}
定时器实现
/**
* @author apdoer
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/3/22 20:33
*/
@Slf4j
public class SystemTimer implements Timer {
/**
* 底层时间轮
*/
private TimeWheel timeWheel;
/**
* 一个Timer只有一个延时队列
*/
private DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
/**
* 过期任务执行线程
*/
private ExecutorService workerThreadPool;
/**
* 轮询delayQueue获取过期任务线程
*/
private ExecutorService bossThreadPool;
public SystemTimer() {
this.timeWheel = new TimeWheel(1, 20, System.currentTimeMillis(), delayQueue);
this.workerThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
this.bossThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
//20ms推动一次时间轮运转
this.bossThreadPool.submit(() -> {
for (; ; ) {
this.advanceClock(20);
}
});
}
public void addTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
if (!timeWheel.add(entry)) {
//已经过期了
TimerTask timerTask = entry.getTimerTask();
log.info("=====任务:{} 已到期,准备执行============",timerTask.getDesc());
workerThreadPool.submit(timerTask);
}
}
@Override
public void add(TimerTask timerTask) {
log.info("=======添加任务开始====task:{}", timerTask.getDesc());
TimerTaskEntry entry = new TimerTaskEntry(timerTask, timerTask.getDelayMs() + System.currentTimeMillis());
timerTask.setTimerTaskEntry(entry);
addTimerTaskEntry(entry);
}
/**
* 推动指针运转获取过期任务
*
* @param timeout 时间间隔
* @return
*/
@Override
public synchronized void advanceClock(long timeout) {
try {
TimerTaskList bucket = delayQueue.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (bucket != null) {
//推进时间
timeWheel.advanceLock(bucket.getExpiration());
//执行过期任务(包含降级)
bucket.clear(this::addTimerTaskEntry);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("advanceClock error");
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
//todo
return 0;
}
@Override
public void shutdown() {
this.bossThreadPool.shutdown();
this.workerThreadPool.shutdown();
this.timeWheel = null;
}
}
存储任务的环形链表
/**
* @author apdoer
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/3/22 19:26
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
class TimerTaskList implements Delayed {
/**
* TimerTaskList 环形链表使用一个虚拟根节点root
*/
private TimerTaskEntry root = new TimerTaskEntry(null, -1);
{
root.next = root;
root.prev = root;
}
/**
* bucket的过期时间
*/
private AtomicLong expiration = new AtomicLong(-1L);
public long getExpiration() {
return expiration.get();
}
/**
* 设置bucket的过期时间,设置成功返回true
*
* @param expirationMs
* @return
*/
boolean setExpiration(long expirationMs) {
return expiration.getAndSet(expirationMs) != expirationMs;
}
public boolean addTask(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
boolean done = false;
while (!done) {
//如果TimerTaskEntry已经在别的list中就先移除,同步代码块外面移除,避免死锁,一直到成功为止
entry.remove();
synchronized (this) {
if (entry.timedTaskList == null) {
//加到链表的末尾
entry.timedTaskList = this;
TimerTaskEntry tail = root.prev;
entry.prev = tail;
entry.next = root;
tail.next = entry;
root.prev = entry;
done = true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* 从 TimedTaskList 移除指定的 timerTaskEntry
*
* @param entry
*/
public void remove(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
synchronized (this) {
if (entry.getTimedTaskList().equals(this)) {
entry.next.prev = entry.prev;
entry.prev.next = entry.next;
entry.next = null;
entry.prev = null;
entry.timedTaskList = null;
}
}
}
/**
* 移除所有
*/
public synchronized void clear(Consumer<TimerTaskEntry> entry) {
TimerTaskEntry head = root.next;
while (!head.equals(root)) {
remove(head);
entry.accept(head);
head = root.next;
}
expiration.set(-1L);
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return Math.max(0, unit.convert(expiration.get() - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if (o instanceof TimerTaskList) {
return Long.compare(expiration.get(), ((TimerTaskList) o).expiration.get());
}
return 0;
}
}
存储任务的容器entry
/**
* @author apdoer
* @version 1.0
* @date 2021/3/22 19:26
*/
@Data
class TimerTaskEntry implements Comparable<TimerTaskEntry> {
private TimerTask timerTask;
private long expireMs;
volatile TimerTaskList timedTaskList;
TimerTaskEntry next;
TimerTaskEntry prev;
public TimerTaskEntry(TimerTask timedTask, long expireMs) {
this.timerTask = timedTask;
this.expireMs = expireMs;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
void remove() {
TimerTaskList currentList = timedTaskList;
while (currentList != null) {
currentList.remove(this);
currentList = timedTaskList;
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(TimerTaskEntry o) {
return ((int) (this.expireMs - o.expireMs));
}
}
任务包装类(这里也可以将工作任务以线程变量的方式去传入)
@Data
@Slf4j
class TimerTask implements Runnable {
/**
* 延时时间
*/
private long delayMs;
/**
* 任务所在的entry
*/
private TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry;
private String desc;
public TimerTask(String desc, long delayMs) {
this.desc = desc;
this.delayMs = delayMs;
this.timerTaskEntry = null;
}
public synchronized void setTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
// 如果这个timetask已经被一个已存在的TimerTaskEntry持有,先移除一个
if (timerTaskEntry != null && timerTaskEntry != entry) {
timerTaskEntry.remove();
}
timerTaskEntry = entry;
}
public TimerTaskEntry getTimerTaskEntry() {
return timerTaskEntry;
}
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("============={}任务执行", desc);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持码农之家。
纯JavaScript实现实时反馈系统时间
用javascript反馈系统时间
运用知识
JavaScript HTML DOM
HTML DOM 中的setInterval() 方法会不停地调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
语法setInterval(code,milliseconds)
code——代码(可以为函数)
milliseconds——在此调用的时间(毫秒)
因此,我们想让反馈的系统时间动起来,只需要让方法没隔1000毫秒调用一次就可以使显示的时间像闹钟一样动起来。
setInterval(function(){myTimer()},1000)
new Date()//获得当前时间
.toLocaleTimeString()//根据本地时间把Date对象的时间部分转换为字符串
.getElementById("clock")//返回带有指定 ID 的元素
.innerHTML=c; //将c返回给指定元素
代码部分
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="clock"></div>
</body>
<script>
var a = setInterval(function(){myTimer()},1000);
function myTimer(){
var b = new Date();
var c = b.toLocaleTimeString();
document.getElementById("clock").innerHTML=c;
}
</script>
</html>
总结
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的纯JavaScript实现实时反馈系统时间,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对码农之家网站的支持!
java时间戳与日期相互转换工具详解
本文为大家分享了java日期与时间戳相互转换大全,供大家参考,具体内容如下
package com.crm.util;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @author DingJiaCheng
* */
public class DateFormatUtil {
/**
* 时间戳转日期
* @param ms
* @return
*/
public static Date transForDate(Integer ms){
if(ms==null){
ms=0;
}
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date temp=null;
if(ms!=null){
try {
String str=sdf.format(msl);
temp=sdf.parse(str);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 获取晚上9点半的时间戳
*
* @return
*/
public static int getTimes(int day, int hour, int minute) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.add(Calendar.DATE, day);
cal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, hour);
cal.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE, minute);
cal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
return (int) (cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000);
}
/**
* 获取当前时间往上的整点时间
*
* @return
*/
public static int getIntegralTime() {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 1);
cal.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
return (int) (cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000);
}
public static int getIntegralTimeEnd() {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 24);
cal.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 0);
cal.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
return (int) (cal.getTimeInMillis() / 1000);
}
/**
* 时间戳转日期
* @param ms
* @return
*/
public static Date transForDate3(Integer ms){
if(ms==null){
ms=0;
}
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm");
Date temp=null;
if(ms!=null){
try {
String str=sdf.format(msl);
temp=sdf.parse(str);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 时间戳转日期
* @param ms
* @return
*/
public static Date transForDate(Long ms){
if(ms==null){
ms=(long)0;
}
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date temp=null;
if(ms!=null){
try {
String str=sdf.format(msl);
temp=sdf.parse(str);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return temp;
}
public static String transForDate1(Integer ms){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
if(ms!=null){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
public static String transForDate2(Integer ms){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
if(ms!=null){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
public static String transForDate4(Integer ms){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy.MM.dd");
if(ms!=null){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
public static String transForDate5(Integer ms){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
if(ms!=null){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
public static String transForDateInChinese(Integer ms){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
if(ms!=null){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
/**
* 日期转时间戳
* @param date
* @return
*/
public static Integer transForMilliSecond(Date date){
if(date==null) return null;
return (int)(date.getTime()/1000);
}
/**
* 获取当前时间戳
* @return
*/
public static Integer currentTimeStamp(){
return (int)(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000);
}
/**
* 日期字符串转时间戳
* @param dateStr
* @return
*/
public static Integer transForMilliSecond(String dateStr){
Date date = DateFormatUtil.formatDate(dateStr);
return date == null ? null : DateFormatUtil.transForMilliSecond(date);
}
/**
* 日期字符串转时间戳
* @param dateStr
* @return
*/
public static Integer transForMilliSecond(String dateStr,String format){
Date date = DateFormatUtil.formatDate(dateStr,format);
return date == null ? null : DateFormatUtil.transForMilliSecond(date);
}
/**
* 日期字符串转时间戳
* @param dateStr
* @param 格式 如"yyyy-mm-dd"
* @return
*/
public static Integer transForMilliSecondByTim(String dateStr,String tim){
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(tim);
Date date =null;
try {
date = sdf.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date == null ? null : DateFormatUtil.transForMilliSecond(date);
}
/**
* 字符串转日期,格式为:"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
* @param dateStr
* @return
*/
public static Date formatDate(String dateStr){
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date result=null;
try {
result = sdf.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 字符串转日期,格式为:"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
* @param dateStr
* @return
*/
public static Date formatDate(String dateStr,String format){
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(format);
Date result=null;
try {
result = sdf.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 日期转字符串
* @param date
* @return
*/
public static String formatDate(Date date){
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String result=null;
result = sdf.format(date);
return result;
}
/**
* 日期转字符串
* @param date
* @return
*/
public static String formatDate(Date date,String format){
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(format);
String result=null;
result = sdf.format(date);
return result;
}
/**
* 时间戳格式化输出(httl模版用)
*
* @param ms 时间戳
* @param format 格式化
* @return
*/
public static String transForDate(Integer ms, String format){
String str = "";
if(ms!=null){
long msl=(long)ms*1000;
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(format);
if(!ms.equals(0)){
try {
str=sdf.format(msl);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return str;
}
/**
* 取BigDecimal类型数的整数或小数部分(httl模版用)
*
* @param b 值
* @param mode 模式 0取整 1去小数部分
* @return
*/
public static String splitBigDecimal(BigDecimal b, int mode) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
String s = df.format(b);
if(mode==0){
return s.split("\\.")[0];
}else {
return "."+s.split("\\.")[1];
}
}
/**
* 计算两个日期之间差的天数(httl模版用)
*
* @param ts1 时间戳1
* @param ts2 时间戳2
* @return
*/
public static int caculate2Days(Integer ts1, Integer ts2) {
Date firstDate = DateFormatUtil.transForDate(ts1);
Date secondDate = DateFormatUtil.transForDate(ts2);
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(firstDate);
int dayNum1 = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
calendar.setTime(secondDate);
int dayNum2 = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
return Math.abs(dayNum1 - dayNum2);
}
/**
* 给手机加密中间四位加星号
*
* @param mobile
* @return
*/
public String mobileSerect(String mobile){
if(!StringUtils.isBlank(mobile)){
int between = mobile.length()/2;
mobile = mobile.substring(0, between-2)+"****"+mobile.substring(between+2, mobile.length());
}
return mobile;
}
/**
* 给邮箱加密加星号
*
* @param email
* @return
*/
public String emailSerect(String email) {
if(!StringUtils.isBlank(email)){
int length = email.lastIndexOf("@");
email = email.substring(0, 2)+"****"+email.substring(length-2, email.length());
}
return email;
}
/**
* BigDecimal类型数据相加
*
* @param BigDecimal source
* @param BigDecimal target
* @return
*/
public BigDecimal sumBigDicimal(BigDecimal source, BigDecimal target) {
source = source.add(target);
return source;
}
/**
* BigDecimal类型数据相加
*
* @param BigDecimal source
* @param BigDecimal target
* @return
*/
public BigDecimal sumBigDicimalAndDouble(BigDecimal source, Double target) {
BigDecimal new_target = new BigDecimal(target);
source = source.add(new_target);
return source;
}
/**
* BigDecimal类型数据相减
*
* @param BigDecimal source
* @param BigDecimal target
* @return
*/
public BigDecimal subBigDicimal(BigDecimal source, BigDecimal target) {
source = source.subtract(target);
return source;
}
/**
* 获取传入时间和当前时间的时间差
* @return
*/
public static Long getTimediff(int timeStamp){
Date d1 = DateFormatUtil.transForDate(timeStamp);
Date today = new Date();
if(d1.getTime()<today.getTime()){
return null;
}
return (d1.getTime()-today.getTime())/1000;
}
/**
* 获取某周的第一天日期
* @param week 0 当周 1 上一周 -1 下一周
* @return
*/
public static String weekFirstDay(int week){
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
int dow = c1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
c1.add(Calendar.DATE, -dow-7*(week-1)-5 );
String d1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").format(c1.getTime());
return d1+" 00:00:00";
}
/**
* 当前时间加一年
*/
public static String addYear(int startTime){
Date firstDate = DateFormatUtil.transForDate(startTime);
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(firstDate);
calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR,1);
String d1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(calendar.getTime());
return d1;
}
/**
* 获取某周的最后一天日期
* @param week
* @return
*/
public static String weekLastDay(int week){
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
int dow = c1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
c1.add(Calendar.DATE, -dow-7*(week-1)+1);
String d1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").format(c1.getTime());
return d1+" 23:59:59";
}
/**
* 和当前时间比对
* @return
*/
public static boolean greaterThanNow(int timeStamp){
Date d1 = DateFormatUtil.transForDate(timeStamp);
Date today = new Date();
if(d1.getTime()>=today.getTime()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* HH:mm:ss格式时间转换为1970-01-01日的时间戳(也就是只有时间没有日期的情况要求使用时间戳表示时间)
* @author DingJiaCheng
* */
public static int transFromTime(String time){
return transForMilliSecond("1970-01-01 "+time,"yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss");
}
/**
* 时间戳转换为HH:mm:ss格式时间(日期去除)
* @author DingJiaCheng
* */
public static String transToTime(int time){
String s = new String(transForDate1(time));
String ss[] = s.split(" ");
return ss[1];
}
public static int transToChuo(String dateString){
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
int res = 0;
try {
Date date=simpleDateFormat .parse(dateString);
res = (int) date.getTime();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println(getIntegralTimeEnd());
System.out.println(transForDate2(transForMilliSecond("2015-02-25 00:00:00")));
//System.out.println(transForMilliSecond("2016-01-25","yyyy-mm-dd"));
//System.out.println(transForDate1(transForMilliSecond("1970-01-01 00:00:00","yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss")));
//System.out.println(currentTimeStamp());
//System.out.println(transForDate(currentTimeStamp()));
//System.out.println(new Date());
//System.out.println(DateUtils.getDate());
System.out.println(transFromTime("00:00:01"));
System.out.println(transToTime(transFromTime("15:01:13")));
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持码农之家。
参考资料
-
马士兵Java零基础入门到精通
本课程是一门适合纯小白入门的课程,带你从无到有走进java的世界,让你精通java的各种基础知识以及web开发框架,手把手带你敲出企业级实战项目,有问必答,理论与实践相结合教学,带你掌握真正的java核心技术。
大小:13.74 GB马士兵Java
立即下载 -
Java2实用教程(第3版)

《Java2实用教程(第三版)》是2006年8月1日清华大学出版社出版的图书,作者是耿祥义、张跃平。 Java是一种很优秀的编程语言,具有面向对象、与平台无关、安全、稳定和多线程等特点,是目前软件设计中极为健壮的编程语言。Java语言不仅可以用来开发大型的应用程序,而且特别适合于在Internet上应用开发,Java已成为网络时代最重要的编程语言之一。 《Java2实用教程(第3版)》注重可读性和实用性,配备了大量的例题,许多例题都经过精心的考虑,既
大小:51.5 KBJava2
立即下载 -
Java中文文本信息处理:从海量到精准

本书以零基础的用户通过自学进行一个中文分词系统软件做为总体目标。从Java基本英语的语法刚开始,随后到文本处理相关的数据结构和优化算法,*后保持文字分割和词性标注。这书是小有的
大小:290 MBJava
立即下载 -
HTML5+CSS3+JavaScript从入门到精通

本书以基础知识、示例、实战案例相结合的方式详尽讲述了HTML,CSS,JavaScript及目前最新的前端技术
大小:186 MBweb开发
立即下载 -
Java EE核心框架实战(第二版)

Java EE核心框架实战 第二版 出版时间:2017 《Java EE核心框架实战(第2版)》的宗旨是提高读者学习Java EE的效率,增强其项目实战能力。为此,本书摒弃了软件公司中不常用或不实用的技术,而是采用近200个开发案例,为读者讲解了开发商业软件的知识,帮助读者进行“精要”式的学习,汲取Java EE的思想,正确地进行项目实战。《Java EE核心框架实战(第2版)》涵盖了MyBatis 3、Struts 2、Ajax、JSON、jQuery、Spring 4 MVC、Hibernate 5、
大小:24.72MBJava
立即下载 -
Java基础面试题(含答案详解)
最新Java面试题(附答案) WORD 下载
大小:537 KBJava面试
立即下载 -
面向对象软件工程:使用UML、模式与 Java

《面向对象软件工程:使用UML、模式与Java(第3版)》由b.bruegge和a.h.dutoit编写的,是卡耐基梅隆大学(cmu)高年级本科生和研究生的教材。在第3版本中,作者以循序渐进的方式给出一个完
大小:59.5 MB面向对象
立即下载





6小时35分钟前整理