本站精选了一篇相关的编程文章,网友扈傲南根据主题投稿了本篇教程内容,涉及到Python、freegames库、Python、freegames小游戏、Python freegames库相关内容,已被742网友关注,下面的电子资料对本篇知识点有更加详尽的解释。
Python freegames库
简介
- 简介:零代码的22个小游戏集合
- 作者:Grant Jenks
- 版本:2.4.0
- 安装:
D:\>pip install freegames -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
Looking in indexes: https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/
Collecting freegames
Downloading https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/packages/62/f5/643ebe95085f1fea2
d8e4597259d8c56a920df1ed10dcfb65d7b80caff4f/freegames-2.4.0-py3-none-any.whl (10
8 kB)
------------------------------------ 109.0/109.0 kB 528.1 kB/s eta 0:00:00
Installing collected packages: freegames
Successfully installed freegames-2.4.0- 简要说明:
DESCRIPTION
Free Python Games is an Apache2 licensed collection of free Python games
intended for education and fun. The games are written in simple Python code and
designed for experimentation and changes. Simplified versions of several
classic arcade games are included.
Python is one of the top-five most popular programming languages in the world
and available for free from www.python.org. Python includes an extensive
Standard Library distributed with your installation. The Standard Library has a
module called Turtle which is a popular way to introduce programming to
kids. Turtle was part of the original Logo programming language developed by
Wally Feurzig and Seymour Papert in 1966. All of the games in Free Python Games
are implemented using Python and its Turtle module.
Starting in 2012, Free Python Games began as an after school program to teach
programming to inner-city youth. The goal was to have fun as much as it was to
learn. Since then the games have been improved and used in a variety of
settings ranging from classrooms to summer day-camps.
The games run anywhere Python can be installed which includes desktop computers
running Windows, Mac OS, or Linux and older or low-power hardware such as the
Raspberry Pi. Kids across the United States in grades 6th-12th have enjoyed
learning about topics such as encryption and projectile motion through games.
Each game is entirely independent from the others and includes comments along
with a list of exercises to work through with students. Creativity and
flexibility is important. There is no right or wrong way to implement a new
feature or behavior! You never know which games students will engage with best.
Free Python Games supports a command-line interface (CLI). Help for the CLI is
available using::
$ python3 -m freegames --help
The CLI supports three commands: list, copy, and show. For a list of all games
run::
$ python3 -m freegames list
Any of the listed games may be played by executing the Python module from the
command-line. To reference the Python module, combine "freegames" with the name
of the game. For example, to play the "snake" game run::
$ python3 -m freegames.snake
Games can be modified by copying their source code. The copy command will
create a Python file in your local directory which you can edit. For example,
to copy and play the "snake" game run::
$ python3 -m freegames copy snake
$ python3 snake.py
Python includes a built-in text editor named IDLE which can also execute Python
code. To launch the editor and make changes to the "snake" game run::
$ python3 -m idlelib.idle snake.py
- 游戏列表:
D:\>python -m freegames list ant bagels bounce cannon connect crypto fidget flappy guess life madlibs maze memory minesweeper pacman paint pong simonsays snake tictactoe tiles tron
游戏
执行方法 freegames.游戏名
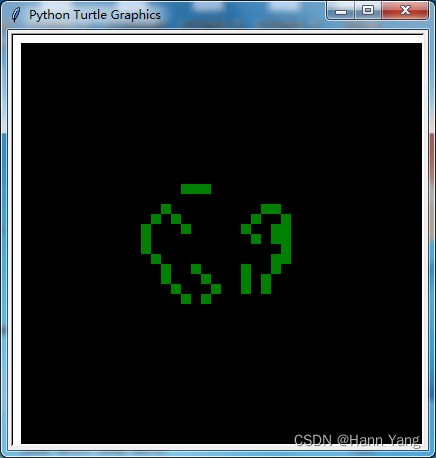
python -m freegames.life
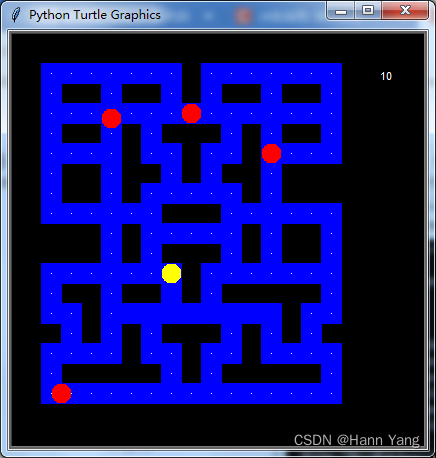
python -m freegames.pacman
python -m freegames.cannon
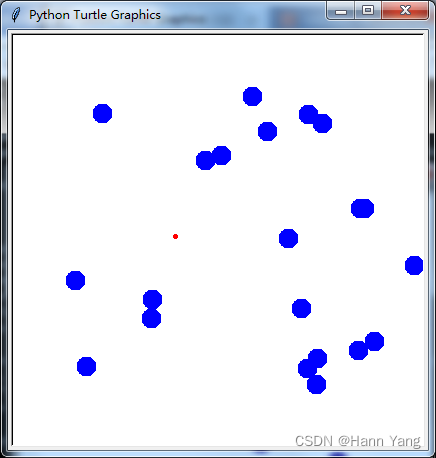
python -m freegames.pong
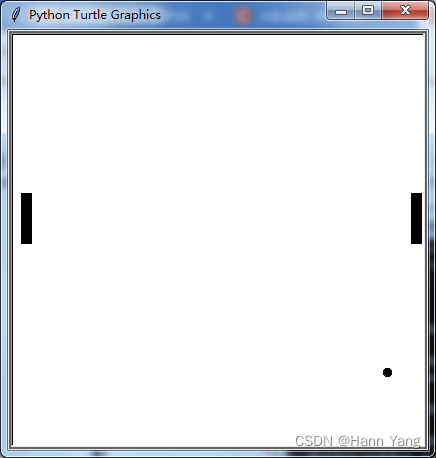
python -m freegames.tiles
python -m freegames.maze
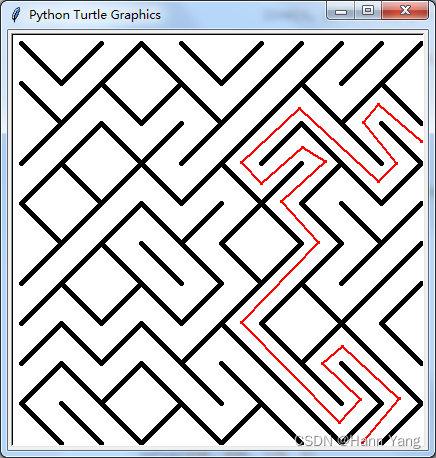
代码学习
所谓“零代码”实际上只是作者帮你写好来,拿来就用或者参考学习而已。
执行: python -m freegames copy maze,就能拷贝出源码来
(Windows系统)执行后,在当前用户的文件夹下保存有源文件: maze.py
源代码:很明显游戏是基于turtle库的代码
"""Maze, move from one side to another.
Excercises
1. Keep score by counting taps.
2. Make the maze harder.
3. Generate the same maze twice.
"""
from random import random
from turtle import *
from freegames import line
def draw():
"""Draw maze."""
color('black')
width(5)
for x in range(-200, 200, 40):
for y in range(-200, 200, 40):
if random() > 0.5:
line(x, y, x + 40, y + 40)
else:
line(x, y + 40, x + 40, y)
update()
def tap(x, y):
"""Draw line and dot for screen tap."""
if abs(x) > 198 or abs(y) > 198:
up()
else:
down()
width(2)
color('red')
goto(x, y)
dot(4)
setup(420, 420, 370, 0)
hideturtle()
tracer(False)
draw()
onscreenclick(tap)
done()再来看一个稍微复杂点的“贪吃蛇”代码:
"""Snake, classic arcade game.
Exercises
1. How do you make the snake faster or slower?
2. How can you make the snake go around the edges?
3. How would you move the food?
4. Change the snake to respond to mouse clicks.
"""
from random import randrange
from turtle import *
from freegames import square, vector
food = vector(0, 0)
snake = [vector(10, 0)]
aim = vector(0, -10)
def change(x, y):
"""Change snake direction."""
aim.x = x
aim.y = y
def inside(head):
"""Return True if head inside boundaries."""
return -200 < head.x < 190 and -200 < head.y < 190
def move():
"""Move snake forward one segment."""
head = snake[-1].copy()
head.move(aim)
if not inside(head) or head in snake:
square(head.x, head.y, 9, 'red')
update()
return
snake.append(head)
if head == food:
print('Snake:', len(snake))
food.x = randrange(-15, 15) * 10
food.y = randrange(-15, 15) * 10
else:
snake.pop(0)
clear()
for body in snake:
square(body.x, body.y, 9, 'black')
square(food.x, food.y, 9, 'green')
update()
ontimer(move, 100)
setup(420, 420, 370, 0)
hideturtle()
tracer(False)
listen()
onkey(lambda: change(10, 0), 'Right')
onkey(lambda: change(-10, 0), 'Left')
onkey(lambda: change(0, 10), 'Up')
onkey(lambda: change(0, -10), 'Down')
move()
done()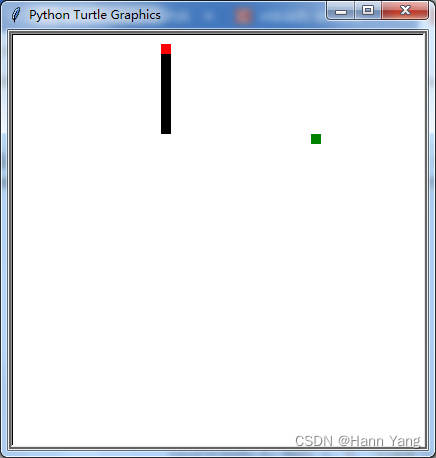
内置类和函数
snake游戏中使用了内置的类vector及函数square
>>> from freegames import square, vector
除了这2个库里还有其它3个:
>>> import freegames >>> freegames.__all__ ['floor', 'line', 'path', 'square', 'vector']
使用简介:
CLASSES
collections.abc.Sequence(collections.abc.Reversible, collections.abc.Collection)
freegames.utils.vector
class vector(collections.abc.Sequence)
| vector(x, y)
|
| Two-dimensional vector.
|
| Vectors can be modified in-place.
|
| >>> v = vector(0, 1)
| >>> v.move(1)
| >>> v
| vector(1, 2)
| >>> v.rotate(90)
| >>> v
| vector(-2.0, 1.0)
|
| Method resolution order:
| vector
| collections.abc.Sequence
| collections.abc.Reversible
| collections.abc.Collection
| collections.abc.Sized
| collections.abc.Iterable
| collections.abc.Container
| builtins.object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __abs__(self)
| v.__abs__() -> abs(v)
|
| >>> v = vector(3, 4)
| >>> abs(v)
| 5.0
|
| __add__(self, other)
| v.__add__(w) -> v + w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v + w
| vector(4, 6)
| >>> v + 1
| vector(2, 3)
| >>> 2.0 + v
| vector(3.0, 4.0)
|
| __eq__(self, other)
| v.__eq__(w) -> v == w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(1, 2)
| >>> v == w
| True
|
| __getitem__(self, index)
| v.__getitem__(v, i) -> v[i]
|
| >>> v = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v[0]
| 3
| >>> v[1]
| 4
| >>> v[2]
| Traceback (most recent call last):
| ...
| IndexError
|
| __hash__(self)
| v.__hash__() -> hash(v)
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> h = hash(v)
| >>> v.x = 2
| Traceback (most recent call last):
| ...
| ValueError: cannot set x after hashing
|
| __iadd__(self, other)
| v.__iadd__(w) -> v += w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v += w
| >>> v
| vector(4, 6)
| >>> v += 1
| >>> v
| vector(5, 7)
|
| __imul__(self, other)
| v.__imul__(w) -> v *= w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v *= w
| >>> v
| vector(3, 8)
| >>> v *= 2
| >>> v
| vector(6, 16)
|
| __init__(self, x, y)
| Initialize vector with coordinates: x, y.
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> v.x
| 1
| >>> v.y
| 2
|
| __isub__(self, other)
| v.__isub__(w) -> v -= w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v -= w
| >>> v
| vector(-2, -2)
| >>> v -= 1
| >>> v
| vector(-3, -3)
|
| __itruediv__(self, other)
| v.__itruediv__(w) -> v /= w
|
| >>> v = vector(2, 4)
| >>> w = vector(4, 8)
| >>> v /= w
| >>> v
| vector(0.5, 0.5)
| >>> v /= 2
| >>> v
| vector(0.25, 0.25)
|
| __len__(self)
| v.__len__() -> len(v)
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> len(v)
| 2
|
| __mul__(self, other)
| v.__mul__(w) -> v * w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v * w
| vector(3, 8)
| >>> v * 2
| vector(2, 4)
| >>> 3.0 * v
| vector(3.0, 6.0)
|
| __ne__(self, other)
| v.__ne__(w) -> v != w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v != w
| True
|
| __neg__(self)
| v.__neg__() -> -v
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> -v
| vector(-1, -2)
|
| __radd__ = __add__(self, other)
|
| __repr__(self)
| v.__repr__() -> repr(v)
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> repr(v)
| 'vector(1, 2)'
|
| __rmul__ = __mul__(self, other)
|
| __sub__(self, other)
| v.__sub__(w) -> v - w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v - w
| vector(-2, -2)
| >>> v - 1
| vector(0, 1)
|
| __truediv__(self, other)
| v.__truediv__(w) -> v / w
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> w / v
| vector(3.0, 2.0)
| >>> v / 2
| vector(0.5, 1.0)
|
| copy(self)
| Return copy of vector.
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = v.copy()
| >>> v is w
| False
|
| move(self, other)
| Move vector by other (in-place).
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v.move(w)
| >>> v
| vector(4, 6)
| >>> v.move(3)
| >>> v
| vector(7, 9)
|
| rotate(self, angle)
| Rotate vector counter-clockwise by angle (in-place).
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> v.rotate(90)
| >>> v == vector(-2, 1)
| True
|
| scale(self, other)
| Scale vector by other (in-place).
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> w = vector(3, 4)
| >>> v.scale(w)
| >>> v
| vector(3, 8)
| >>> v.scale(0.5)
| >>> v
| vector(1.5, 4.0)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| x
| X-axis component of vector.
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> v.x
| 1
| >>> v.x = 3
| >>> v.x
| 3
|
| y
| Y-axis component of vector.
|
| >>> v = vector(1, 2)
| >>> v.y
| 2
| >>> v.y = 5
| >>> v.y
| 5
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| PRECISION = 6
|
| __abstractmethods__ = frozenset()
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from collections.abc.Sequence:
|
| __contains__(self, value)
|
| __iter__(self)
|
| __reversed__(self)
|
| count(self, value)
| S.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value
|
| index(self, value, start=0, stop=None)
| S.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value.
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| Supporting start and stop arguments is optional, but
| recommended.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from collections.abc.Reversible:
|
| __subclasshook__(C) from abc.ABCMeta
| Abstract classes can override this to customize issubclass().
|
| This is invoked early on by abc.ABCMeta.__subclasscheck__().
| It should return True, False or NotImplemented. If it returns
| NotImplemented, the normal algorithm is used. Otherwise, it
| overrides the normal algorithm (and the outcome is cached).
FUNCTIONS
floor(value, size, offset=200)
Floor of `value` given `size` and `offset`.
The floor function is best understood with a diagram of the number line::
-200 -100 0 100 200
<--|--x--|-----|--y--|--z--|-->
The number line shown has offset 200 denoted by the left-hand tick mark at
-200 and size 100 denoted by the tick marks at -100, 0, 100, and 200. The
floor of a value is the left-hand tick mark of the range where it lies. So
for the points show above: ``floor(x)`` is -200, ``floor(y)`` is 0, and
``floor(z)`` is 100.
>>> floor(10, 100)
0.0
>>> floor(120, 100)
100.0
>>> floor(-10, 100)
-100.0
>>> floor(-150, 100)
-200.0
>>> floor(50, 167)
-33.0
line(a, b, x, y)
Draw line from `(a, b)` to `(x, y)`.
path(filename)
Return full path to `filename` in freegames module.
square(x, y, size, name)
Draw square at `(x, y)` with side length `size` and fill color `name`.
The square is oriented so the bottom left corner is at (x, y).另外还有20段代码,你可以用命令自己copy出来一一学习。总体来说,代码难度不是很高,重要的是要自己动手模仿编出新的游戏来!
以上就是Python之freegames 零代码的22个小游戏集合的详细内容,更多关于Python之freegames库的资料请关注码农之家其它相关文章!